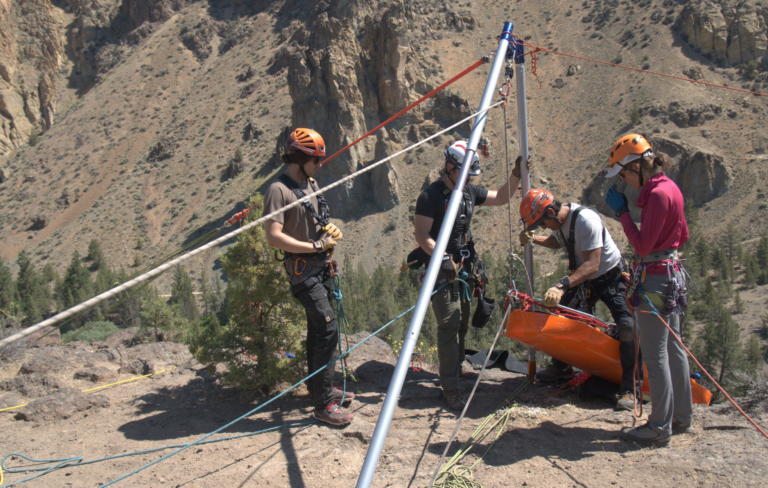
In the dynamic environments of the fire service and search and rescue operations, ensuring the safety of our responders is paramount. Among the critical considerations in these high-risk scenarios is the protection of the rope edge – the lifeline that connects our technicians to safety and facilitates successful rescues.
Rope rescue edge protections encompass a spectrum of techniques and equipment designed not only to safeguard the lives of our responders but also to preserve the integrity of the lifeline itself. At its core, edge protection aims to mitigate the risks associated with four key aspects: travel restraint, fall prevention, work positioning, and fall arrest.
1. Travel Restraint:
Travel restraint measures are essential for preventing technicians from reaching hazardous edges altogether. By employing techniques such as pre-planning, hazard assessments, and the establishment of exclusion zones, responders can avoid exposing themselves to potential fall hazards, thereby minimizing risks to both personnel and equipment.
2. Fall Prevention:
Fall prevention strategies focus on proactive measures to eliminate or mitigate the risk of falls over edges. This includes the use of physical barriers, such as guardrails or covers, to prevent accidental slips or trips. Additionally, the implementation of proper training, including hazard recognition and safe work practices, empowers responders to identify and address potential fall hazards before they occur.
3. Work Positioning:
Work positioning techniques enable responders to safely access and operate in challenging environments near edges. Through the use of specialized equipment, such as positioning lanyards or adjustable work positioning systems, technicians can maintain stable and secure positions while performing critical tasks, minimizing the risk of accidental falls or pendulum swings.
4. Fall Arrest:
In situations where fall hazards cannot be entirely eliminated, fall arrest systems serve as a last line of defense against catastrophic outcomes. These systems, comprising components such as harnesses, lanyards, and energy-absorbing devices, are designed to safely arrest the fall of a technician in the event of a slip or trip over an edge, minimizing the forces exerted on both the rescuer and the rope.
5. Rope Edge Protection Devices:
Introduce various types of edge protection devices specifically designed to safeguard ropes from damage while performing rope rescue operations. These may include edge rollers, rope protectors, edge pads, and edge guards. Highlight their importance in preventing abrasion, cutting, or fraying of the rope caused by sharp edges or rough surfaces.
6. Rope Inspection and Maintenance:
Emphasize the significance of regular inspection and maintenance of ropes used in rescue operations. Discuss the importance of identifying and addressing signs of wear, abrasion, or damage to ropes caused by contact with edges. Provide guidelines for proper rope care, storage, and retirement criteria to ensure the continued safety and reliability of rescue ropes.
7. Integration with Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
Highlight the importance of integrating rope rescue edge protections into existing standard operating procedures (SOPs) and rescue protocols. Emphasize the need for comprehensive training and familiarization with edge protection techniques among responders to ensure consistency and effectiveness in their application during rescue operations.
8. Collaboration with Stakeholders:
Discuss the importance of collaboration with stakeholders, including rope manufacturers, industry experts, and regulatory bodies, in the development and implementation of effective rope rescue edge protection strategies. Encourage ongoing dialogue and knowledge sharing to stay abreast of advancements in edge protection technologies and best practices.
9. Continuous Improvement and Evaluation:
Promote a culture of continuous improvement and evaluation in rope rescue edge protections. Encourage organizations to conduct post-incident reviews and debriefs to identify lessons learned and opportunities for enhancement in edge protection protocols and equipment. Emphasize the value of feedback from frontline responders in driving improvements in rescue operations.
10. Public Awareness and Education:
Advocate for public awareness and education campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of rope rescue edge protections among stakeholders, including emergency responders, employers, and the general public. Provide resources and training materials to promote understanding and adherence to best practices in edge protection to prevent accidents and injuries during rescue operations.
In summary, rope rescue edge protections are crucial for ensuring the safety of responders and the integrity of rescue operations in both fire service and search and rescue contexts. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing travel restraint, fall prevention, work positioning, and fall arrest techniques. Additionally, the use of specialized edge protection devices, regular rope inspection and maintenance, integration with SOPs, collaboration with stakeholders, continuous improvement, and public awareness initiatives are essential components of effective edge protection strategies. By prioritizing rope edge protection, organizations can enhance the safety and effect
Peace on your Days
Lance