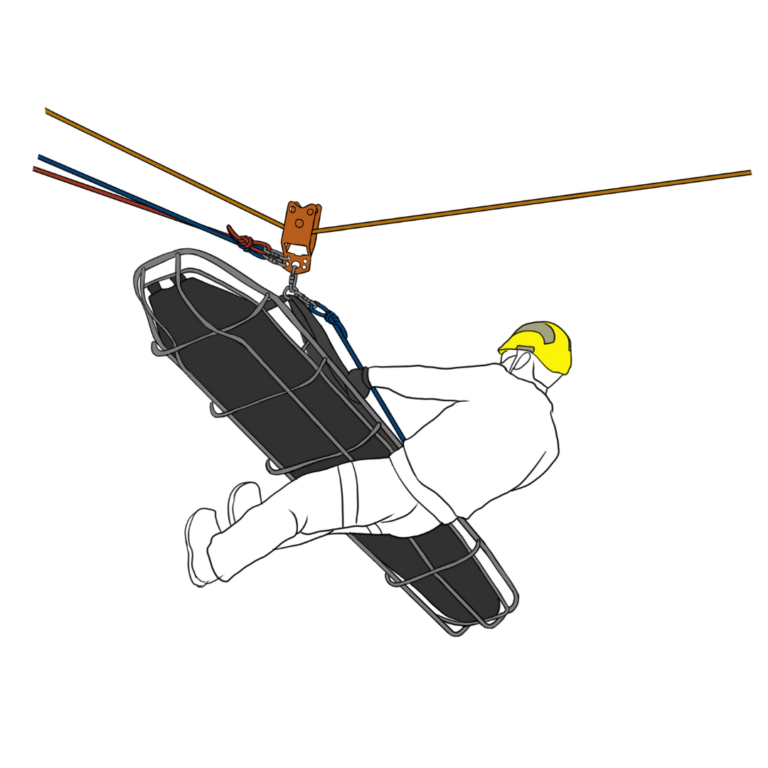
Expanding on Guiding Line and Skate Block Systems in Rope Rescue Operations
In rope rescue operations, guiding line systems and skate block systems are essential techniques for safely navigating challenging environments. These systems ensure the safe transportation of loads, such as stretchers, over obstacles and difficult terrains, reducing risks for both rescuers and patients. Below is an expanded exploration of their applications, setup, and operational considerations.

Guiding Line Systems
Applications
Guiding line systems merge a descent mechanism with a tensioned rope to safely lower a stretcher while maintaining a safe distance from obstructions. These systems are particularly beneficial in:
- Rocky Terrains: Where protrusions could hinder smooth transportation.
- Urban Structures: Navigating debris or architectural obstacles.
- Industrial Sites: Overcoming obstructions like pipeways or machinery.
Setup and Configuration
- Anchor System
- Secure a robust anchor point at the top, using high-strength tie-offs or other reliable connection methods.
- Ensure the anchor is positioned high enough to provide clearance for the stretcher to bypass obstacles.
- Guiding Line Placement
- Establish the guide rope at a higher level than the descent launch point (e.g., anchoring above a window for urban rescues).
- Pass the guideline to the lower team, using a line gun, messenger line, or rappel if necessary.
- Mechanical Advantage System
- Use a mechanical advantage (MA) system, such as a 5:1 or 3:1, depending on available manpower and terrain steepness.
- Position the bottom anchor farther from the slope to increase the lift and tension.
- Primary and Safety Lines
- Attach a primary lowering line and a safety (belay) line to the stretcher harness.
- Use a high-line carriage or large pulley to guide the stretcher along the track.
- Tensioning and Adjustments
- Apply sufficient tension to the guiding line to keep the stretcher clear of obstacles.
- Adjust tension dynamically as the litter moves to account for changes in terrain or proximity to surfaces.

 Load Primarily on the Lowering Line Load Primarily on the Lowering Line |
 Load Primarily on the Guiding Line Load Primarily on the Guiding Line |
Operational Considerations
- Maintaining Safety Distance: Ensure the tension is adequate to keep the litter from colliding with walls or other obstructions.
- Dynamic Adjustments: Elevate the litter when navigating over obstacles and lower it when close to the ground.
- Team Coordination: Clear communication between the top and bottom teams is crucial for seamless operations.
Skate Block Systems
Applications
The skate block system is a streamlined approach for lowering loads from vertical structures such as towers, where traditional guiding lines may not be as efficient. It is particularly useful in:
- Tower Rescues: Navigating tall communication or power structures.
- Industrial Rescues: Simplifying operations in facilities with structural obstructions.
- Speed and Efficiency: Ideal for scenarios requiring rapid deployment with fewer personnel.
 Skate Block with a back-up device belay Skate Block with a back-up device belay |
 Skate Block System Skate Block System |
Setup and Configuration
- Anchor and Pulley System
- Install a directional pulley at the top anchor point.
- Thread the descending rope through the pulley to the lowering device at the base.
- Skate Block Pulley
- Attach an additional pulley (skate block) to the descent line near the subject or litter.
- This pulley redirects the load, pulling it away from the structure during descent.
- Control Lines
- Use the same ropes for load control and descent, eliminating the need for a separate guideline.
- Anchor Positioning
- Place the lower anchor at an optimal distance from the base to maintain a 15-30 degree angle for smooth operation.
Operational Considerations
- Load Stability: Connect both ropes at the same harness point to avoid unbalanced rocking motions.
- System Efficiency: Dual tension systems allow a single rescuer to manage both lines simultaneously if Clutches are used.
- Hauling Adjustments: For upward movement, use a change-of-direction pulley and a ground-level hauling system.
Comparing Guiding Line and Skate Block Systems
| Feature | Guiding Line System | Skate Block System |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Low-angle, horizontal operations | Vertical operations with structural separation |
| Rope Usage | Separate guiding line and descent line | Same ropes for control and descent |
| Anchor Position | Flexible (top or bottom tensioning) | Requires precise lower anchor placement |
| Personnel Requirement | Requires more personnel for setup | Can be operated by a single rescuer |
| Efficiency | Suited for complex terrain | Ideal for quick, straightforward operations |
Best Practices
- Pre-Operational Checks: Inspect all components and connections thoroughly before deployment.
- Load Distribution: Maintain even load distribution across all lines and anchor points.
- Training: Regularly practice setup and operation to ensure proficiency in real scenarios.
- Equipment Maintenance: Keep all gear clean, functional, and compliant with safety standards.
- Communication: Establish clear protocols and signals for seamless teamwork.
Conclusion
Both guiding line and skate block systems are invaluable tools in rope rescue operations, offering versatility and efficiency in diverse scenarios. By mastering these advanced techniques, rescue teams can navigate challenging environments while prioritizing safety and effectiveness. These systems empower teams to respond confidently, ensuring successful outcomes in critical situations.
Peace on your Days,
Lance
Peace on your Days
Lance